MAPS-X
Sampling-based random-tree algorithms for MRMP are extended to consider plan interpretability and thus producing more easily validated plans.
Traditional Multi-Robot Motion Planning (MRMP) focuses on computing trajectories for multiple robots acting in an environment, such that the robots do not collide when the trajectories are taken simultaneously. In safety-critical applications, a human supervisor may want to verify that the plan is indeed collision-free. In this work, we propose a notion of explanation for a plan of MRMP, based on visualization of the plan as a short sequence of images representing time segments, where in each time segment the trajectories of the agents are disjoint, clearly illustrating the safety of the plan. We show that standard notions of optimality (e.g., makespan) may create conflict with short explanations. Thus, we propose meta-algorithms, namely Multi-Agent Plan Segmenting-\(X\) (MAPS-\(X\)) and its lazy variant, that can be plugged onto existing coupled sampling-based tree planners \(X\) to produce plans with good explanations using a desirable number of images. We demonstrate the efficacy of this explanation-planning scheme and extensively evaluate the performance of MAPS-\(X\). An example of MAPS-X is shown below.
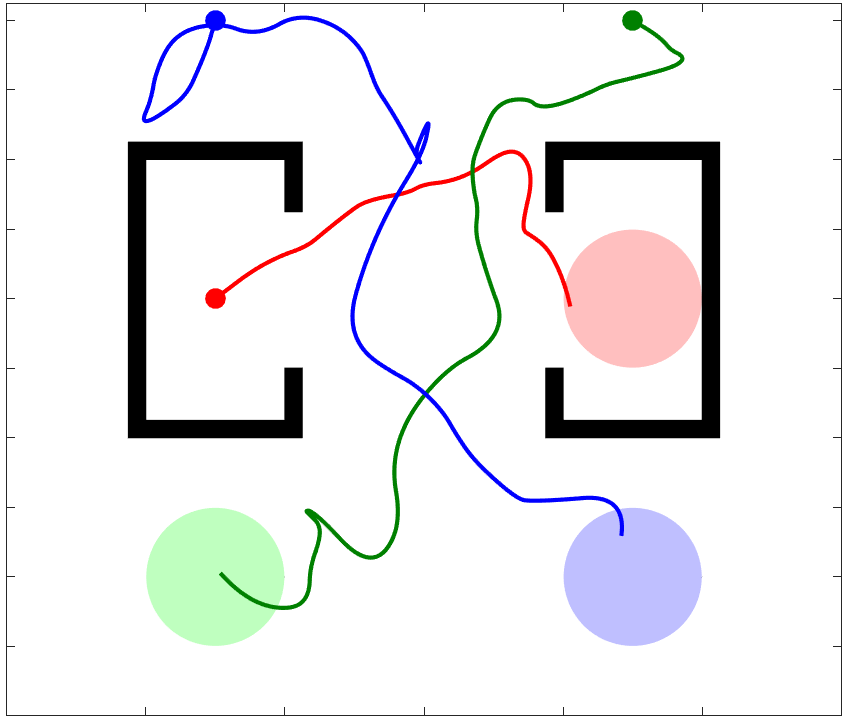
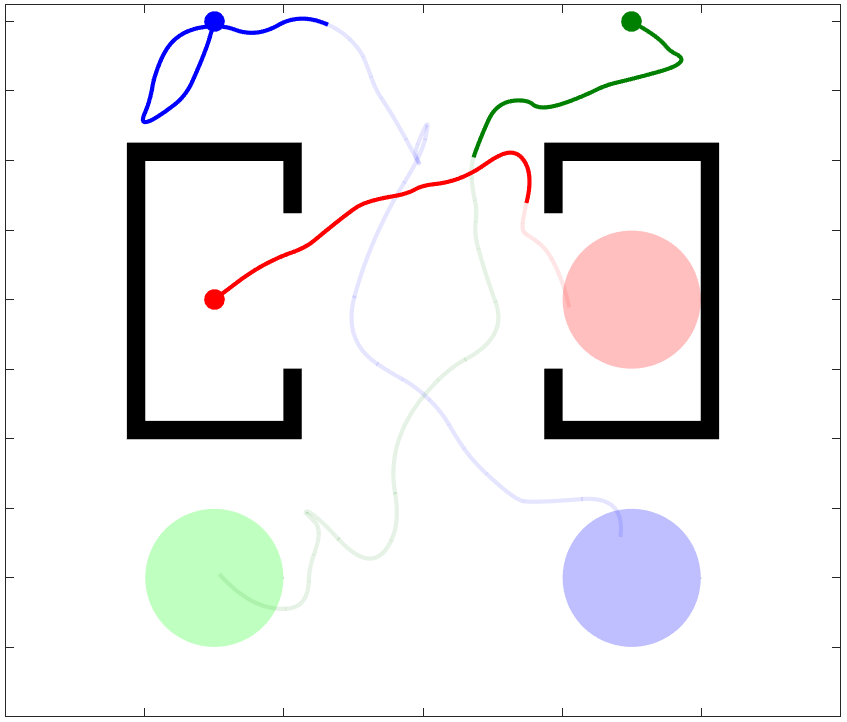
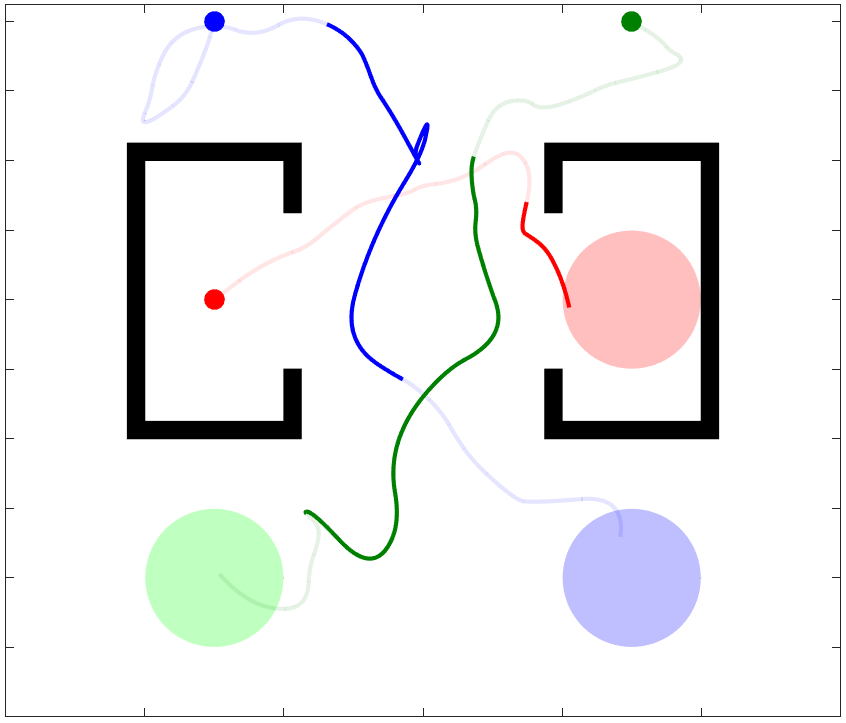
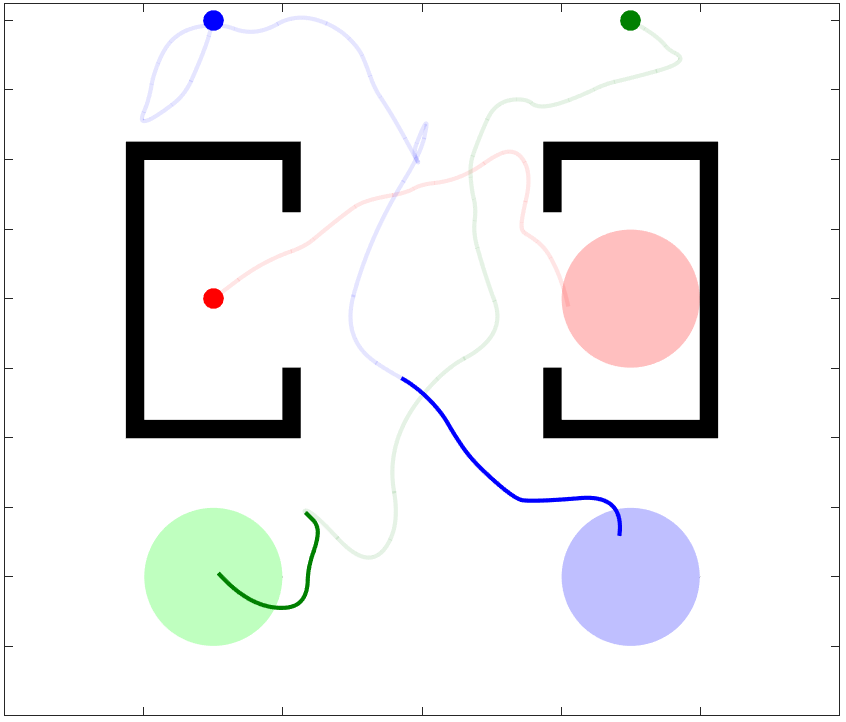
I invite you to investigate any of these great resources to learn more about K-CBS:
- The original MAPS-\(X\) ICRA 2021 Conference Paper
- The implementation of MAPS-\(X\)